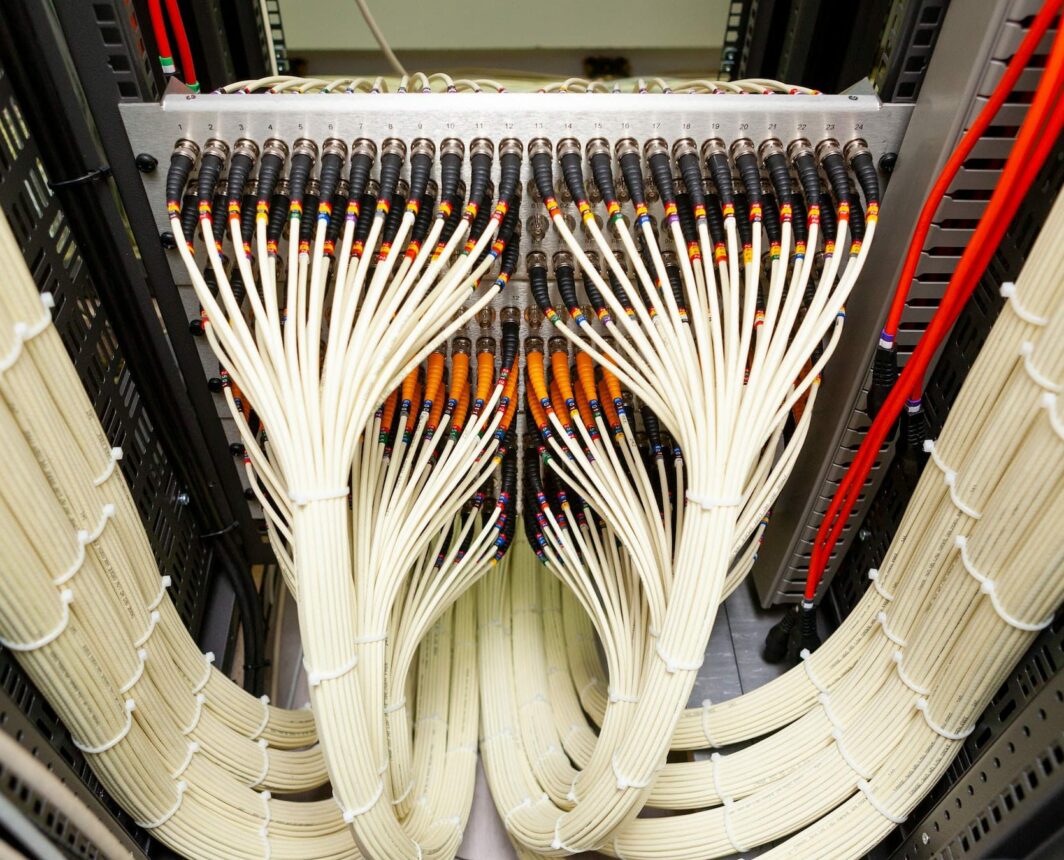
Horizontal Cabling
Horizontal cabling is how most data cabling connects within your network system. The wires bridge your workspace to the network’s central hub and typically end in a termination, where the cables plug into a device. Horizontal cabling also includes standard outlets and areas where cables transition between two types.
Vertical Cabling
Vertical cabling, also called “backbone cabling,” provides the structure for cables to interconnect between various telecommunication rooms. While horizontal cables connect the hub to work areas, vertical cabling connects multiple hubs.
Entrance Facility Structured Cabling
Entrance facility cabling involves the components necessary for each building’s network to connect to an outside telecommunications provider or private network. This cabling system can also connect vertical cabling between different buildings.
Consolidation Point Structured Cabling
The consolidation point for data cabling systems is typically a central (sometimes environmentally-controlled) room containing all the major network equipment, including servers and routers. Smaller networks may use a standard telecommunications room or entrance facility instead.
Telecommunications Enclosure
The telecommunications enclosure (or room) is where horizontal and vertical cabling systems terminate and cross over via connecting equipment. These enclosures contain several network components, such as patch cords and auxiliary equipment.
Work Area Components
These components are the ones your network users, or employees, interact with daily and are the endpoint for horizontal cabling. Work area components include patch cables, outlets, data cables, and PC adapters to enable workstation equipment functionality like computers, phones, and printers.